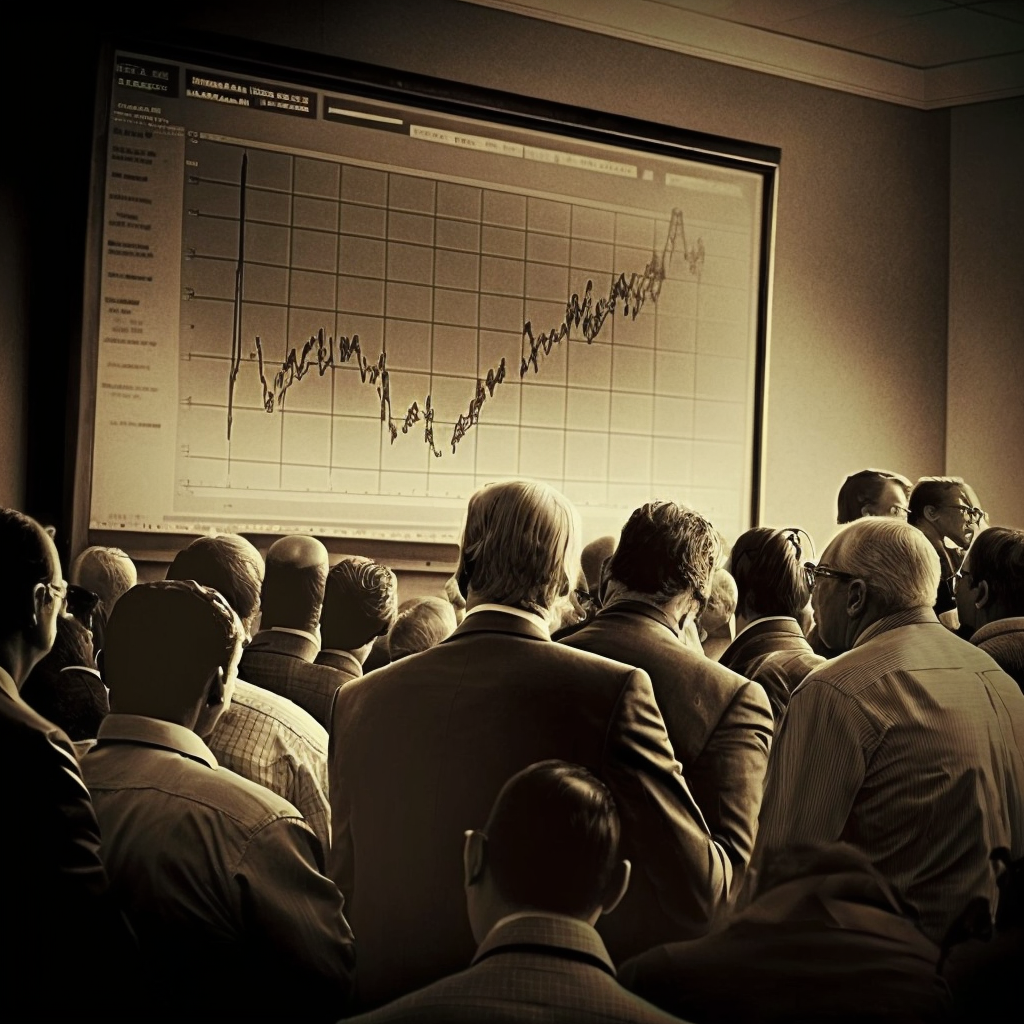
UK Inflation Rate Drops to 8.7% From 10.1% In March 2023
Synopsis
Discover how the United Kingdom experiences its sharpest decline in inflation, offering a glimmer of hope amidst economic uncertainty. Uncover the factors behind this decrease, the implications for the economy, and the crucial areas that demand attention. Engage with expert insights to navigate the path towards economic stability.

Key Takeaways
- UK inflation experienced its sharpest decline since the cost of living crisis began, with the annual rate dropping to 8.7% from 10.1% in April 2023.
- The absence of record energy price increases contributed to the decrease in inflation, but food prices continued to rise at the fastest pace in 45 years.
- The decline in inflation is expected to prompt the Bank of England to implement further interest rate hikes
- While the decline offers temporary relief, the current inflation rate still exceeds the Bank of England's target of 2.0%
- Electricity and gas prices played a significant role in driving down inflation
- Chancellor Jeremy Hunt expressed concern over the persistent rise in food prices
UK Inflation Drops to 8.7%
The United Kingdom has been grappling with a persistent cost of living crisis in recent years, with soaring inflation rates burdening households and straining the economy. However, there is finally a ray of hope on the horizon. In April 2023, the nation witnessed the sharpest fall in inflation since the crisis began, as the annual rate dropped to 8.7% from a staggering 10.1%. While this decline provides a momentary respite, challenges remain. In this article, we will explore the factors behind the fall in inflation, the implications for the economy, and the critical areas where further progress is needed.

Price Changes Which Reduced UK Inflation to 8.7% In April 2023
One key factor contributing to the drop in UK inflation is the absence of record energy price increases that had burdened households the previous year. The positive impact of this development was somewhat offset by the relentless rise in food prices, which continued to surge at the fastest pace in 45 years. In the 12 months leading up to April, food and non-alcoholic drink prices skyrocketed by 19.1%, placing additional strain on consumers' wallets. Although City economists had anticipated a larger decline to 8.2% in April, the fact that inflation fell below double digits for the first time since August is an encouraging sign.
.jpg)
Detailed Analysis of April 2023 Inflation Figures
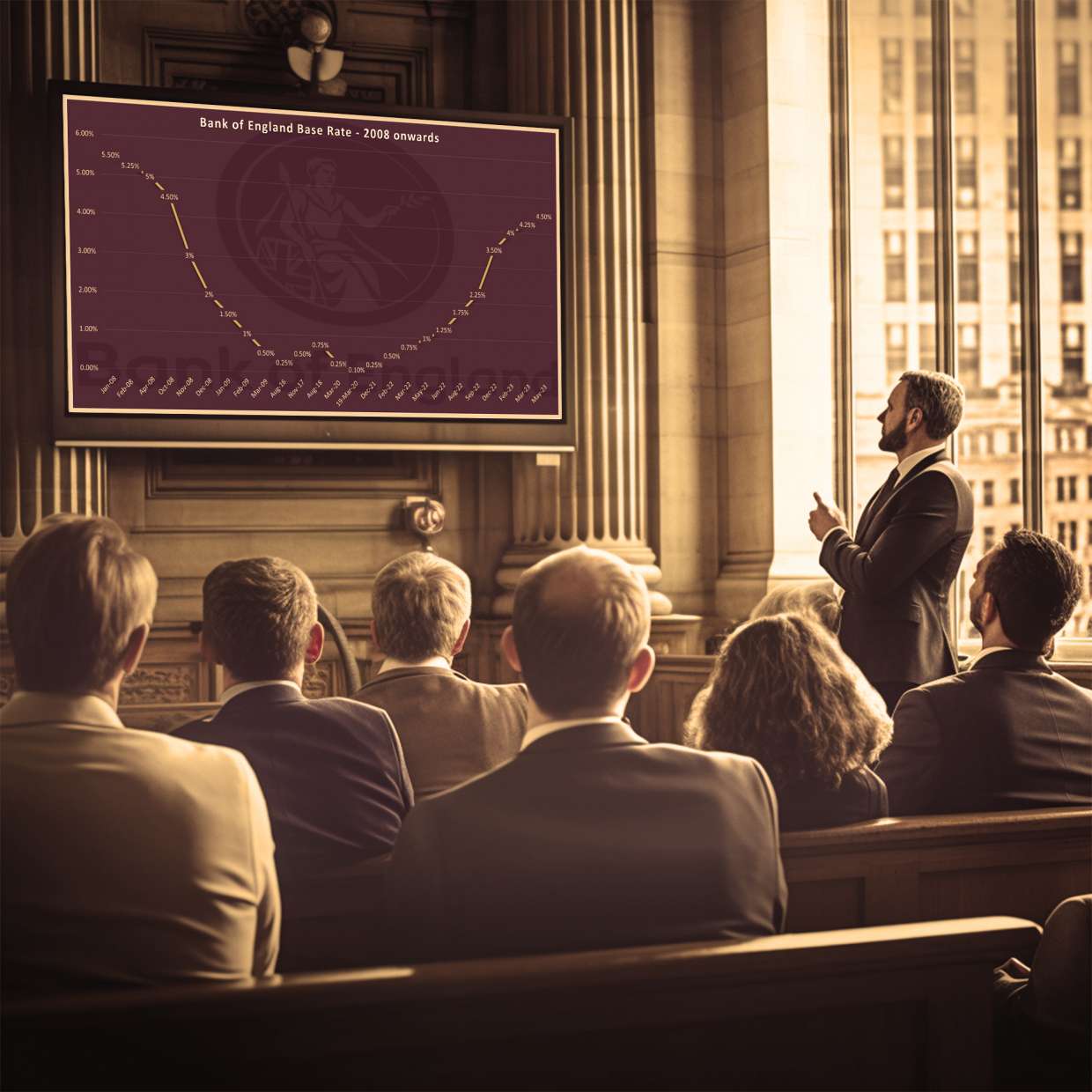
The sharp decline in inflation is expected to reinforce the belief that the Bank of England will implement further interest rate hikes during its next meeting in June. This move signifies the most aggressive assault on inflation witnessed in decades. The central bank had previously projected a drop in inflation to 8.4% in April, and the actual figures indicate progress, albeit not as significant as initially anticipated. Despite this relief, it is crucial to recognise that the current inflation rate far exceeds the Bank of England's target of 2.0%, emphasising the need for continued vigilance.
Upon examining the latest data from the Office for National Statistics (ONS), it becomes evident that electricity and gas prices played a significant role in driving down the annual inflation rate, contributing to a decline of 1.4 percentage points. This decrease was due to the omission of last April's rise in the Ofgem price cap from the calculation. However, this positive development was somewhat dampened by other factors such as the continued rise in food prices, as well as increasing costs for recreation and culture, alcoholic beverages and tobacco, communication, and transport.
Response From Chancellor Jeremy Hunt
In response to the inflation figures, Chancellor Jeremy Hunt acknowledged the positive progress made in tackling inflation, particularly with regard to it falling into single digits. However, Hunt expressed concern over the persistent rise in food prices, which he noted is still occurring at an alarming rate. Acknowledging the praise from the International Monetary Fund (IMF) regarding decisive action against inflation, Hunt emphasised the need to address the issue of escalating food prices, indicating that more work needs to be done to fully alleviate the burden on consumers.
.jpg)
A Ray of Hope in the Battle Against UK Inflation
Looking beyond the April 2023 inflation figures, it is imperative to analyze the broader landscape. While the decline in inflation offers a beacon of hope, the path to achieving sustainable economic stability remains arduous. The Bank of England must maintain a proactive stance in combating inflation and diligently monitor key sectors, particularly the volatile food and energy markets. However, it is essential to recognise that the battle against inflation is far from won. The current inflation rate, though reduced, still remains significantly higher than the Bank of England's target of 2.0%. The bank must strike a judicious equilibrium, raising interest rates sufficiently to curb inflationary pressures while ensuring that such actions do not stifle economic growth or burden businesses and households disproportionately.
Related Articles
This guide and its content is copyright of Chard (1964) Ltd - © Chard (1964) Ltd 2024. All rights reserved. Any redistribution or reproduction of part or all of the contents in any form is prohibited.
We are not financial advisers and we would always recommend that you consult with one prior to making any investment decision.
You can read more about copyright or our advice disclaimer on these links.